|
RDFAnalysis
0.1.1
Physics analysis with ROOT::RDataFrame
|
|
RDFAnalysis
0.1.1
Physics analysis with ROOT::RDataFrame
|
The central idea of this package is to model an analysis as a series of operations on the data in a ROOT TTree, arranged in a tree structure (note that 'tree' here refers to the data structure which is a distinct concept to ROOT's TTree). There are three main types of transformation in an analysis
Applying new selections can create a branching structure as different filters divide the initial set of events into multiple regions.
As an example, consider an analysis looking for the Zγ production with the subsequent decay Z → l+l-. The analysis wishes to separate this into electron and muon decays, then fill histograms with the di-lepton mass spectrum in both cases. A very basic tree structure for this analysis would be
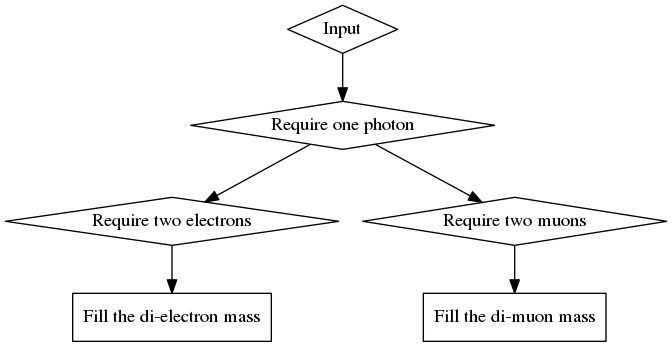
where diamonds represent filters and squares represent fills. This convention will be used throughout the rest of this document. When they appear, defines will be represented by ovals.